[ Introduction ]
You are about to start "Algebra II" Lesson. Algebra II is the continuation of Algebra I. About 20% of the Algebra II will be related to Geometry so it will be good to take Algebra II after you take Geometry. However, if you are a motivated student then you can take Geometry and Algebra II simultaneously. If you plan to go to 4 year University, then I strongly recommend you to take Algebra II.
There will be 28 Lessons for Algebra II. (25 Algebra II Math Standards + 3 Probability and Statistics Math Standards) Compared to Algebra I, there are several topics that are very new - Complex Number, Logarithm, Conic Sections, and Series.
Downloads: Algebra II - CST Released Test*
Algebra II - CST Blueprint*
Before you start Lesson #1, I want you to read Readme page again.
[ Lesson #1 - Absolute Value Equations ] **
Math Standards 1.0 - Students solve equations and inequalities involving absolute value.
Mr. Kwon's Comment - This Lesson #1 Topic is Easy! When it is absolute value equation, you need to setup two equations and solve for x. When it is absolute value inequality, you need to remember my lesson about "Sandwich for <" and "Outside for >". One thing you need to be careful is that the Inequality is Reversed when you multiply or divide by negative number to both sides. This Lesson #1 has 2 STAR rating. **
Let's review Algebra I,
#1. Solve: 11 + 3x - 7 = 6x + 5 - 3x
#2. Solve: 6x + 5 - 2x = 4 + 4x + 1
Can you find the solution (answer)? If you can't, you need to review Algebra I. #1 - No Solution, #2 - Any # for x (Infinitely many solutions)
[ Key Concept - Absolute Value Equations / Inequality ]

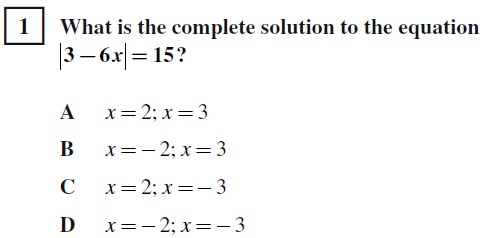 |  |
There are 2 problems (Type C) related to this Lesson #1 from CST Released Test (Algebra II). They are very easy. You must know how to solve both of above.
#1. Set up two equations to solve. --> 3-6x = 15 ; 3-6x= -15. --> Solve for x. x=-2 ; x=3. --> Answer=B
#2. Set up two equations. --> 12-4x = 2 or 12-4x = -2 --> x=10/4=2.5 or x=14/4=7/2=3.5. --> Answer=D
Type B problems have "Inequalities with Absolute Values" as below.
 | #8b. Solve Inequality. 2|5x – 1| + 6 < 20.
|
#8 above is from CST Released Test (Algebra I). Funny thing here is that Algebra II problems (#1, #2 above) were easier than #8 from Algebra I.
#8. Hint: -5 both sides --> divides by -1 both sides (do not forget that the inequality is reversed when you multiply or divide by nagative) --> |x+4| >= 8 --> Outside! --> x+4 >= 8 or x+4 <= -8. --> x>=4 or x <= -12 --> Answer=D (Note: It looked like "Sandwich" but it was "Outside" because of negative of -|x+4|)
#8b. Hint: -6 both sides --> divides by 2 both sides --> |5x-1| < 7 --> Sandwich! --> -7 < 5x-1 < 7 --> +1 to everywhere --> -6 < 5x < 8 --> divide by 5 to everywhere --> -6/5 < x < 8/5 is the Answer.
Do you need Type A problems??? Solve #1A, 2A below and check your answer with Mr. Kwon.
#1A. What is the solution to the equation |x - 2| + 2x = 1?
#2A. What is the solution to the equation |x - 12| = -20?
[ YouTube Video Lesson #1 - Absolute Value Equations ]
[ Lesson #2 - System of Linear Equations ] ****
Math Standards - 2.0 Students solve systems of linear equations and inequalities (in two or three variables) by substitution, with graphs, or with matrices.
Mr. Kwon's Comment - This Lesson #2 Topic is Important! I think this topic is also easy except the Word Problems (#3, #5 below).
1. When it is system of linear equations with multiple choices, you can use "substitution" or "linear combination method" or "Plug-in~ Plug-in~" the answer to ALL of the orginal equations. (Backward solving).
2. When you see "True statement", it is "Infinitely many solutions" (they are exactly the same lines).
3. When you see "False statement", it is "No solution" (they are parallel).
4. For system of linear inequalities, you need to be careful with inequality (either dotted or solid line) and shade above or below of the line on the graph. (up or below from the y-intercept)
5. When it is 3 variable system problem, try to find "no solution" or "infinitely many solution" by observing/comparing all of 3 equations "carefully" to see if any of two look similar. If not, use "Backward solving" to save time.
6. Word Problems - You need to read the problems carefully in order to understand how to set up the system of linear equations (2 variables). My advice here is to remember "Practice makes perfect".
Recall that there are 2 problems about Lesson #1 (Absolute Value Equations) from CST Released Test (Algebra II). There are 7 problems related to this Lesson #2 (System of Linear Equations/Inequalities) from CST. This Lesson #2 has 4 STAR rating. ****
Out of 7 problems, there is only one problem of "3 variable system" and 6 problems are 2 variable systems. 3 out of 7 are system of linear inequalities. There are two word problems related to system of linear equations (Type B) and other problems are Type C.
#9 (Type C) below is system of linear equations with 2 variables and #7 (Type B) is system of linear inequalities with 2 variables.
 |  |
#9. above can be solved in several ways. (substitution method, linear combination, plug-in~) Answer=C.
#7. can be solved in two ways. (1. Graph the solution and find which point is inside of that shaded region, 2. Plug-in~ Plug-in~ and find the true statement for both inequalities) I choose Plug-in~. If you plug A(-4,-1)=(x,y) into the first inequality, then 2 >= -6 True! If you plug (-4,-1) into the 2nd inequality, then 10 < -6 False! so A is not the answer. Let's try B(3,1). -1 >= -6 True! -7 < -6 True! Both inequalities work so Answer is B.
 |  |
Above #6 (Type C) and #8 (Type B) are the "System of linear inequalities with 2 variables".
#6. Both of them are dotted lines. y>-2 because it is shaded above. y<x+1 because it is shaded below of y-intercept 1. Answer=B
#8. Both of them are solid lines. It will be good to have y=mx+b form to understand the graph of the line. Notice that it is shaded above the y-intercept 3 (y >= 3) and below of y-intercept -2 (y <= -2). Answer=D.
 |  |
Above #4 (Type BC) and #4b (Type BC) are the "System of linear equations with 3 variables". Read Mr. Kwon's comment #5.
#4. Observe 3 equations carefully then you will see the 1st equation and the 3rd equation look similar. So multiply -3 to the 1st equation. -6x+3y-9z=-24 vs. -6x+3y-9z=24. They are PARALLEL! No solution!
#4b. Observe 3 equations carefully then you will see the 1st equation and the 3rd equation look similar. (also 1st vs. 2nd and 2nd vs. 3rd) So multiply -3 to the 3rd equation. 9x+3y+3z=-12 vs. 9x+3y+3z=-12. They are IDENTICAL! Many solution!
If you can not find any similarities between any two lines(planes), then it will be more efficient to use "Plug-in~" method for 3 variables in multiple choice problems. --> It is not proper way but short-cut!
 |  |
Above #3 (Type B) and #5 (Type A) are the "Word Problems for System of linear equations". #5 is harder to understand than #3.
First of all, you need to read the question word by word "To Set up Two Linear Equations". Once you setup two equations, you can solve it for unknown variables.
#3. Set R=# rose and C=# carnation. R+C=17. 15R + 8C = 192 (because rose costs $15 and carnation costs $8) Solve the system of linear equations with 2 variables (R, C). Multiply 8 to 1st equation --> 8R+8C=136. --> Subtract from 2nd equation --> 7R = 56 --> R=8 --> Answer=C.
#5. Set A=# of 6 bagel-package and B= # of 12 bagel-package. A+B=20. 6A+12B=168. Solve the system by multiplying 6 to the 1st equation. --> 6A+6B=120 --> Subtract from 2nd equation --> 6B=48 --> B=8. --> Answer=B.
For Word Problems, it will take more time to solve (set up and solve it) compared to other problems so I recommend you to solve these problems at the end. First skip and solve other easy problems and come back to this problem later when you take CST exam.
 |  |
Above two problems are Type A problems for Lesson #2.
5A+. is Type A+ and you can also solve the system of linear equations using "Inverse Matrix"
If you major math, computer science or engineering at University, then you will learn "Linear Algebra" that involves with Matrix (Matrices) everyday and this topic is the foundation of computer 3D graphics.

[ YouTube Video Lesson #2 - System of Linear Equations ]
[ Lesson #3 - Polynomial Division ] *** STAR
Math Standards 3.0 - Students are adept at operations on polynomials, including long division.
Mr. Kwon's Comment - This Lesson #3 Topic is very easy like Lesson #1 (Absolute Value Equations). Lesson #3 is about Polynomial Operations (+-*/) but I want to name it as "Polynomial Division" because the addition, subtraction and multiplication of polynomials are the same things that we learned from Algebra I. We did not learn Polynomial (long) division but this will be easy as long as you do not make a mistake. Poly means "Many" and "~nomial" means "Terms".
Recall that there are 2 problems about Lesson #1 (Absolute Value Equations) from CST Released Test (Algebra II). 7 problems about Lesson #2 (System of Linear Equations/Inequalities).
There are 6 problems about Lesson #3 (Polynomial +, -, x, division) from CST. - 4 problems about multiplications, 1 about division, 1 about add/subtract. This Lesson #3 has 3 STAR rating. ***
 |  |
#11. (Type C) Polynomial Multiplication. You need to multiply 6 times (3x2). A and C are not the answer because -4x-5=20. --> Answer=B.
#12. (Type C) Polynomial Add/Subtract. Remember "Distributive Property" of Algebra I. Answer=D.
 |  |
#13. (Type C) Polynomial Multiplication. Be careful that this is not (a-b)(a+b) form. Answer=D.
#15. (Type C) Polynomial Multiplication. 2 by 3 = 6 times. Answer is either B or C (-2x*-8=16x). Answer=C.
 |  |
#10. (Type B) Polynomial Divisioin. B is not the answer. Answer=D. 2x+7 is called "Divisor". 2x^4+21x^3+35x^2-37x+46 is called "Dividend". x^3+7x^2-7x+6 is called "Quotient". 4 is the "Remainder". There is a short-cut to find a answer. (Answer D: 7 is the last # of divisor, 6 is the last # of quotient --> 7*6=42 and 42 + 4(remainder) = 46(dividend's last #). --> If you understand this short-cut, then it is Type A problem.
#14. (Type B) Polynomial Multiplication. Volume=Width*Length*Height = (x+4)(x+1)(x+6). --> Answer=B.
 |  |
#10b. (Type B) Polynomial Divisioin. Notice that Dividend 2x^3 - 48 does not have x^2 term and x term. It will be good to add 0x^2 + 0x when you do long division. Answer=C. There are two short-cuts to solve this problem. If you used "Remainder Theorem", then it is Type A problem. 2(27)-48=54-48=6.
#10c. (Type B) Polynomial Division. You can use short-cut and remainder is 0 so it can be factored. --> Answer=B.

[ YouTube Video Lesson #3 - Polynomial Division ]
[ Lesson #4 - Factoring ] ***** STAR
Math Standards 4.0 - Students factor polynomials representing the difference of squares, perfect square trinomials, and the sum and difference of two cubes.
[ Lesson #7 - Rational Expressions ] *****
Math Standards 7.0 - Students add, subtract, multiply, divide, reduce, and evaluate rational expressions with monomial and polynomial denominators and simplify complicated rational expressions, including those with negative exponents in the denominator.
Mr. Kwon's Comment - I will combine Lesson #4 (Factoring) and Lesson #7 (Rational Expressions) because Lesson #7 mainly involves with factoring. "Rational" means "Fraction" or "Fractional". Lesson #7 is about Polynomials in a Fractional Form -Both numerator and denominator are polynomials and you need to simplify that fraction using factoring. The hard part of Lesson #7 is that you need to remember everything about fraction (how to make LCD - least common denominator) and how to apply to polynomial settings. Lesson #17 also includes negative exponents in fraction but I will assume that you already mastered "exponents" from Algebra I. (review Algebra I if necessary)
Recall that there are 2 problems about Lesson #1 (Absolute Value Equations) from CST Released Test (Algebra II). 7 problems about Lesson #2 (System of Linear Equations/Inequalities). 6 problems about Lesson #3 (Polynomial +, -, x, division).
There are 13 problems about Lesson #4 (5 out of 13) and Lesson #7 (8 out of 13 are fractions; 3 of them are negative exponents) from CST. This Lesson (#4 and #7) has 5 STAR rating. *****
[ Key Concept - Factoring ]
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
 |  |
Above 5 problems are about "Factoring". We did not learn #16 (Type B) "Cubic Factoring" in Algebra I but we learned #17-20 (Type BC). Most of problems in CST test are "Stright forward" that means you can find the answer right away using formula. You do not need to ponder. However, SAT problems are not straight forward and you need a strategy to attack most of problems.
#16. (Type B) I want you to memorize this formula or understand how this formula was created. (I explained this in classroom) --> Answer=D.
#17. (Type C) a^2-b^2=(a-b)(a+b) factoring. --> Answer=A.
#18. (Type C) a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b) factoring. --> Answer=D.
#19. (Type B) a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b) factoring. First step is to take 3 out as factor. 3(4x^2-49) --> Answer =D.
#20. (Type C) a^2-2ab+b^2=(a-b)^2 factoring. --> Answer =A.
#19b. (Type B) a^2-b^2=(a+b)(a-b) factoring. First step is to take 0.01 out as factor. 0.01(x^2-81) --> Answer =D.
[ Key Concept - Rational Expressions ]
 |  |
 |  |
#25. (Type C) Factor each part and cancel --> x(x+4)/(x+3) * (x-3)(x+3)/(x+4)(x-3)--> Answer=B.
#27. (Type C) Factor each aprt and cancel --> 2x(x-5)/(x+4)^2 * 4(x+4)/(x-5)(x+5) --> Answer =C.
 |  |
#24. (Type AB) Factor each part and cancel --> Note (2-x)=-(x-2) This manipluation is important in SAT--> 4(x-2)(x+2) / -(x-2) --> Answer=D.
#26. (Type C) Separate into three fractions --> x^2+4xy+4y^2 = (x+2y)^2 --> Answer =B.
 |  |
#21. (Type B) LCD=(x+5)(x-2), Numerator is (x+3)(x-2) + 6. --> Answer=A.
#28. (Type C) Factoring -2x-2y=-2(x+y) and cancel some of terms --> Answer =A.
 |  |
#22. (Type C) Answer=A. #23. (Type C) Answer=D. You must know how to change from negative exponent to positive exponent by "Reciprocal". (denominator-->numerator, numerator-->denominator after changing the sign)

[ Lesson #5 Imaginary Number 1 ] **** STAR
Math Standards 5.0 - Students demonstrate knowledge of how real and complex numbers are related both arithmetically and graphically. In particular, they can plot complex numbers as points in the plane.
[ Lesson #6 Imaginary Number 2 ] **** STAR
Math Standards 6.0 - Students add, subtract, multiply, and divide complex numbers.
Mr. Kwon's Comment - I will combine Lesson #5 and Lesson #6 (Imaginary Number) because both of them mainly involves with imaginary number (complex number). Instead of calling "Complex Number" as lesson title, I would prefer calling this lesson as "Imaginary Number". "Complex Number" is "a+bi form" and bi part is "Imaginary Number". Lesson #5 is very easy and it is like locating a point in the X-Y plane. X-axis is real number part which is "a" of "a+bi" and Y-axis is imaginary number part which is "b" of "a+bi".
Lesson #5-#6 is about Complex Number Operations (+-*/) and you can imagine complex number as "binomial" (example: 3+5y) and do the operation for add/subtract/multiply. To divide two complex numbers, you must multiply the numerator and denominator by the complex conjugate of the denominator. (it is called "Rationalize the denominator")
Recall that there are 2 problems about Lesson #1 (Absolute Value Equations) from CST Released Test (Algebra II). 7 problems about Lesson #2 (System of Linear Equations/Inequalities). 6 problems about Lesson #3 (Polynomial +, -, x, division). 13 problems about Lesson #4 & #7 (Factoring and Rational Expressions).
There are 9 problems about Lesson #5 (2 of 9) and #6 (7 of 9) of Imaginary Number. This Lesson (#5 and #6) has 4 STAR rating. ****
[ Key Concept - Complex Number ]

 |  |
#29. (Type C) Imagine 5-2i --> (5,-2)=(x,y). Imagine Real=X and Imaginary=Y. --> Answer=D.
#31. (Type C) (x,y)=(3,-4) --> 3-4i --> Answer =C. Easy enough?
 |  |
#30. (Type C) Recall the property of exponents. i^4 = (i^2)^2 = (-1)^2 = 1 --> Answer=C.
#32. (Type C) Recall i^2=-1 by the definition of i. 24i^2 = 24(-1) = -24 --> Answer=C.
 |  |
#36. (Type C) Use "Distributive Property" and treat i as variable (like x or y) --> Answer=D.
#37. (Type C) Treat i as variable. --> Answer=A. So easy!
 |  |
#34. (Type BC) Easy to get the answer but this is important to use (a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2 for complex conjugates --> 9-i^2=9+1=10 --> Remember! When you multiply the complex number conugates together, it becomes real number. --> Answer=B.
#33b. (Type B) Multiply conjugate --> (8-6i)(3-i) / (3+i)(3-i) = (18-26i)/10 = (9-13i)/5 --> Answer=C.
 |  |
#33. (Type C) Use (a+b)(a-b)=a^2-b^2 for complex conjugates --> Multiply (3-i) both to denominator and numerator --> 2(3-i) / (3+i)(3-i) --> 2(3-i)/10 = (3-i)/5 --> Answer=B.
#33b. (Type B) Multiply conjugate (a-bi) to both --> (a-bi) / (a+bi)(a-bi) = (a-bi) / (a^2+b^2) --> Answer=B.
 |  |
#32b. (Type C) i^2=-1. Use Exponent Property. --> i^8 = (i^2)^4 = (-1)^4 = 1 --> Answer=D.
#34b. (Type BC) Multiply first two & multiply the third --> 5(-5+6i) = -25+30i --> Answer=B.
[ YouTube Video Lesson #5 - Imaginary Number ]
[ Lesson #8 - Quadratic Equations ]
Math Standards 8.0 - Students solve and graph quadratic equations by factoring, completing the square, or using the quadratic formula. Students apply these techniques in solving word problems. They also solve quadratic equations in the complex number system.
[ Lesson #9-10 - Quadratic Functions ]
Math Standards 9.0 - Students demonstrate and explain the effect that changing a coefficient has on
the graph of quadratic functions; that is, students can determine how the graph
of a parabola changes as a, b, and c vary in the equation y = a(x-b) 2+ c.
Math Standards 10.0 - Students graph quadratic functions and determine the maxima, minima, and zeros of the function.

[ Lesson #11, 13-14 Log Log Log ]
Math Standards 11.0 - Students prove simple laws of logarithms. (11.1 Students understand the inverse relationship between exponents and logarithms and use this relationship to solve problems involving logarithms and exponents. 11.2 Students judge the validity of an argument according to whether the properties of real numbers, exponents, and logarithms have been applied correctly at each step.)
Math Standards 13.0 - Students use the definition of logarithms to translate between logarithms in any base.
Math Standards 14.0 - Students understand and use the properties of logarithms to simplify logarithmic
numeric expressions and to identify their approximate values.
[ Lesson #12 - Rational Exponents ]
Math Standards 12.0 Students know the laws of fractional exponents, understand exponential functions, and use these functions in problems involving exponential growth and decay.
[ Lesson #15 - Definitions ]
Math Standards 15.0 - Students determine whether a specific algebraic statement involving rational
expressions, radical expressions, or logarithmic or exponential functions is sometimes
true, always true, or never true.

[ Lesson #16 Conic Sections 1 ]
Math Standards 16.0 - Students demonstrate and explain how the geometry of the graph of a conic
section (e.g., asymptotes, foci, eccentricity) depends on the coefficients of the
quadratic equation representing it.
[ Lesson #17 Conice Sections 2 ]
Math Standards 17.0 - Given a quadratic equation of the form ax2 + by2 + cx + dy + e = 0, students can use the method for completing the square to put the equation into standard form and can recognize whether the graph of the equation is a circle, ellipse, parabola, or hyperbola. Students can then graph the equation.
[ Lesson #18-20 Counting ]
Math Standards 18.0 - Students use fundamental counting principles to compute combinations and
permutations.
Math Standards 19.0 - Students use combinations and permutations to compute probabilities.

[ Lesson #20 - Pascal Triangle ]
Math Standards 20.0 - Students know the binomial theorem and use it to expand binomial expressions that are raised to positive integer powers.
[ Lesson #21 - Math Induction ]
Math Standards 21.0 - Students apply the method of mathematical induction to prove general statements about the positive integers.
[ Lesson #22-23 Series ]
Math Standards 22.0 - Students find the general term and the sums of arithmetic series and of both
finite and infinite geometric series.
Math Standards 23.0 - Students derive the summation formulas for arithmetic series and for both finite and infinite geometric series.
[ Lesson #24-25 Functions ]
Math Standards 24.0 - Students solve problems involving functional concepts, such as composition,
defining the inverse function and performing arithmetic operations on functions.
Math Standards 25.0 Students use properties from number systems to justify steps in combining and
simplifying functions.
 |  |
[ Lesson #26-28 Probability & Statistics ]
Prob & Stat Standards 1.0 - Students know the definition of the notion of independent events and can use the rules for addition, multiplication, and complementation to solve for probabilities of particular events in finite sample spaces.
Prob & Stat Standards 2.0 - Students know the definition of conditional probability and use it to solve for probabilities in finite sample spaces.
Prob & Stat Standards 7.0 - 7.0 Students compute the variance and the standard deviation of a distribution of data.